File size: 39,267 Bytes
660379f e3a68be af2b4b5 3b8ef86 78a1cf9 3b8ef86 d609877 e3a68be 660379f af2b4b5 effad5d af2b4b5 effad5d af2b4b5 effad5d af2b4b5 effad5d af2b4b5 effad5d af2b4b5 effad5d af2b4b5 effad5d af2b4b5 effad5d af2b4b5 effad5d 24ce340 effad5d af2b4b5 effad5d af2b4b5 effad5d af2b4b5 24ce340 3fef804 af2b4b5 3fef804 24ce340 3fef804 af2b4b5 3fef804 af2b4b5 3fef804 af2b4b5 3fef804 af2b4b5 3fef804 af2b4b5 78a1cf9 af2b4b5 78a1cf9 af2b4b5 78a1cf9 af2b4b5 78a1cf9 af2b4b5 78a1cf9 af2b4b5 78a1cf9 af2b4b5 78a1cf9 af2b4b5 78a1cf9 af2b4b5 78a1cf9 af2b4b5 78a1cf9 af2b4b5 78a1cf9 af2b4b5 78a1cf9 af2b4b5 78a1cf9 af2b4b5 78a1cf9 af2b4b5 64454d4 af2b4b5 64454d4 af2b4b5 64454d4 af2b4b5 64454d4 af2b4b5 64454d4 af2b4b5 64454d4 78a1cf9 af2b4b5 e68e2a4 af2b4b5 24ce340 af2b4b5 24ce340 af2b4b5 24ce340 af2b4b5 24ce340 af2b4b5 24ce340 af2b4b5 24ce340 af2b4b5 24ce340 af2b4b5 24ce340 af2b4b5 24ce340 af2b4b5 24ce340 |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 307 308 309 310 311 312 313 314 315 316 317 318 319 320 321 322 323 324 325 326 327 328 329 330 331 332 333 334 335 336 337 338 339 340 341 342 343 344 345 346 347 348 349 350 351 352 353 354 355 356 357 358 359 360 361 362 363 364 365 366 367 368 369 370 371 372 373 374 375 376 377 378 379 380 381 382 383 384 385 386 387 388 389 390 391 392 393 394 395 396 397 398 399 400 401 402 403 404 405 406 407 408 409 410 411 412 413 414 415 416 417 418 419 420 421 422 423 424 425 426 427 428 429 430 431 432 433 434 435 436 437 438 439 440 441 442 443 444 445 446 447 448 449 450 451 452 453 454 455 456 457 458 459 460 461 462 463 464 465 466 467 468 469 470 471 472 473 474 475 476 477 478 479 480 481 482 483 484 485 486 487 488 489 490 491 492 493 494 495 496 497 498 499 500 501 502 503 504 505 506 507 508 509 510 511 512 513 514 515 516 517 518 519 520 521 522 523 524 525 526 527 528 529 530 531 532 533 534 535 536 537 538 539 540 541 542 543 544 545 546 547 548 549 550 551 552 553 554 555 556 557 558 559 560 561 562 563 564 565 566 567 568 569 570 571 572 573 574 575 576 577 578 579 580 581 582 583 584 585 586 587 588 589 590 591 592 593 594 595 596 597 598 599 600 601 602 603 604 605 606 607 608 609 610 611 612 613 614 615 616 617 618 619 620 621 622 623 624 625 626 627 628 629 630 631 632 633 634 635 636 637 638 639 640 641 642 643 644 645 646 647 648 649 650 651 652 653 654 655 656 657 658 659 660 661 662 663 664 665 666 667 668 669 670 671 672 673 674 675 676 677 678 |
---
library_name: peft
base_model: tiiuae/falcon-7b-instruct
license: apache-2.0
language:
- en
pipeline_tag: text-generation
datasets:
- EmbeddingStudio/query-parsing-instructions-falcon
tags:
- search-queries
- instruct-fine-tuned
- search-queries-parser
- zero-shot
- llm
- falcon
inference: false
---
# Model Card for the Query Parser LLM using Falcon-7B-Instruct
EmbeddingStudio is the [open-source framework](https://github.com/EulerSearch/embedding_studio/tree/main), that allows you transform a joint "Embedding Model + Vector DB" into
a full-cycle search engine: collect clickstream -> improve search experience-> adapt embedding model and repeat out of the box.
It's a highly rare case when a company will use unstructured search as is. And by searching `brick red houses san francisco area for april`
user definitely wants to find some houses in San Francisco for a month-long rent in April, and then maybe brick-red houses.
Unfortunately, for the 15th January 2024 there is no such accurate embedding model. So, companies need to mix structured and unstructured search.
The very first step of mixing it - to parse a search query. Usual approaches are:
* Implement a bunch of rules, regexps, or grammar parsers (like [NLTK grammar parser](https://www.nltk.org/howto/grammar.html)).
* Collect search queries and to annotate some dataset for NER task.
It takes some time to do, but at the end you can get controllable and very accurate query parser.
EmbeddingStudio team decided to dive into LLM instruct fine-tuning for `Zero-Shot query parsing` task
to close the first gap while a company doesn't have any rules and data being collected, or even eliminate exhausted rules implementation, but in the future.
The main idea is to align an LLM to being to parse short search queries knowing just a company market and a schema of search filters. Moreover, being oriented on applied NLP,
we are trying to serve only light-weight LLMs a.k.a `not heavier than 7B parameters`.
## Model Details
### Model Description
This is only [Falcon-7B-Instruct](https://huggingface.co/tiiuae/falcon-7b-instruct) aligned to follow instructions like:
```markdown
### System: Master in Query Analysis
### Instruction: Organize queries in JSON, adhere to schema, verify spelling.
#### Category: Logistics and Supply Chain Management
#### Schema: ```[{"Name": "Customer_Ratings", "Representations": [{"Name": "Exact_Rating", "Type": "float", "Examples": [4.5, 3.2, 5.0, "4.5", "Unstructured"]}, {"Name": "Minimum_Rating", "Type": "float", "Examples": [4.0, 3.0, 5.0, "4.5"]}, {"Name": "Star_Rating", "Type": "int", "Examples": [4, 3, 5], "Enum": [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]}]}, {"Name": "Date", "Representations": [{"Name": "Day_Month_Year", "Type": "str", "Examples": ["01.01.2024", "15.06.2023", "31.12.2022", "25.12.2021", "20.07.2024", "15.06.2023"], "Pattern": "dd.mm.YYYY"}, {"Name": "Day_Name", "Type": "str", "Examples": ["Monday", "Wednesday", "Friday", "Thursday", "Monday", "Tuesday"], "Enum": ["Monday", "Tuesday", "Wednesday", "Thursday", "Friday", "Saturday", "Sunday"]}]}, {"Name": "Date_Period", "Representations": [{"Name": "Specific_Period", "Type": "str", "Examples": ["01.01.2024 - 31.01.2024", "01.06.2023 - 30.06.2023", "01.12.2022 - 31.12.2022"], "Pattern": "dd.mm.YYYY - dd.mm.YYYY"}, {"Name": "Month", "Type": "str", "Examples": ["January", "June", "December"], "Enum": ["January", "February", "March", "April", "May", "June", "July", "August", "September", "October", "November", "December"]}, {"Name": "Quarter", "Type": "str", "Examples": ["Q1", "Q2", "Q3"], "Enum": ["Q1", "Q2", "Q3", "Q4"]}, {"Name": "Season", "Type": "str", "Examples": ["Winter", "Summer", "Autumn"], "Enum": ["Winter", "Spring", "Summer", "Autumn"]}]}, {"Name": "Destination_Country", "Representations": [{"Name": "Country_Name", "Type": "str", "Examples": ["United States", "Germany", "China"]}, {"Name": "Country_Code", "Type": "str", "Examples": ["US", "DE", "CN"]}, {"Name": "Country_Abbreviation", "Type": "str", "Examples": ["USA", "GER", "CHN"]}]}]```
#### Query: Which logistics companies in the US have a perfect 5.0 rating ?
### Response:
[{"Value": "Which logistics companies in the US have a perfect 5.0 rating?", "Name": "Correct"}, {"Name": "Customer_Ratings.Exact_Rating", "Value": 5.0}, {"Name": "Destination_Country.Country_Code", "Value": "US"}]
```
**Important:** Additionally, we are trying to fine-tune the Large Language Model (LLM) to not only parse unstructured search queries but also to correct spelling.
- **Developed by EmbeddingStudio team:**
* Aleksandr Iudaev [[LinkedIn](https://www.linkedin.com/in/alexanderyudaev/)] [[Email](mailto:[email protected])]
* Andrei Kostin [[LinkedIn](https://www.linkedin.com/in/andrey-kostin/)] [[Email](mailto:[email protected])]
* ML Doom [AI Assistant]
- **Funded by EmbeddingStudio team**
- **Model type:** Instruct Fine-Tuned Large Language Model
- **Model task:** Zero-shot search query parsing
- **Language(s) (NLP):** English
- **License:** apache-2.0
- **Finetuned from model:** [Falcon-7B-Instruct](https://huggingface.co/tiiuae/falcon-7b-instruct)
- **!Maximal Length Size:** we used 1024 for fine-tuning, this is highly different from the original model `max_seq_length = 2048`
- **Tuning Epochs:** 3 for now, but will be more later.
**Disclaimer:** As a small startup, this direction forms a part of our Minimum Viable Product (MVP). It's more of
an attempt to test the 'product-market fit' rather than a well-structured scientific endeavor. Once we check it and go with a round, we definitely will:
* Curating a specific dataset for more precise analysis.
* Exploring various approaches and Large Language Models (LLMs) to identify the most effective solution.
* Publishing a detailed paper to ensure our findings and methodologies can be thoroughly reviewed and verified.
We acknowledge the complexity involved in utilizing Large Language Models, particularly in the context
of `Zero-Shot search query parsing` and `AI Alignment`. Given the intricate nature of this technology, we emphasize the importance of rigorous verification.
Until our work is thoroughly reviewed, we recommend being cautious and critical of the results.
### Model Sources
- **Repository:** code of inference the model will be [here](https://github.com/EulerSearch/embedding_studio/tree/main)
- **Paper:** Work In Progress
- **Demo:** Work In Progress
## Uses
We strongly recommend only the direct usage of this fine-tuned version of [Falcon-7B-Instruct](https://huggingface.co/tiiuae/falcon-7b-instruct):
* Zero-shot Search Query Parsing with porived company market name and filters schema
* Search Query Spell Correction
For any other needs the behaviour of the model in unpredictable, please utilize the [original mode](https://huggingface.co/tiiuae/falcon-7b-instruct) or fine-tune your own.
### Instruction format
```markdown
### System: Master in Query Analysis
### Instruction: Organize queries in JSON, adhere to schema, verify spelling.
#### Category: {your_company_category}
#### Schema: ```{filters_schema}```
#### Query: {query}
### Response:
```
Filters schema is JSON-readable line in the format (we highly recommend you to use it):
List of filters (dict):
* Name - name of filter (better to be meaningful).
* Representations - list of possible filter formats (dict):
* Name - name of representation (better to be meaningful).
* Type - python base type (int, float, str, bool).
* Examples - list of examples.
* Enum - if a representation is enumeration, provide a list of possible values, LLM should map parsed value into this list.
* Pattern - if a representation is pattern-like (datetime, regexp, etc.) provide a pattern text in any format.
Example:
```json
[{"Name": "Customer_Ratings", "Representations": [{"Name": "Exact_Rating", "Type": "float", "Examples": [4.5, 3.2, 5.0, "4.5", "Unstructured"]}, {"Name": "Minimum_Rating", "Type": "float", "Examples": [4.0, 3.0, 5.0, "4.5"]}, {"Name": "Star_Rating", "Type": "int", "Examples": [4, 3, 5], "Enum": [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]}]}, {"Name": "Date", "Representations": [{"Name": "Day_Month_Year", "Type": "str", "Examples": ["01.01.2024", "15.06.2023", "31.12.2022", "25.12.2021", "20.07.2024", "15.06.2023"], "Pattern": "dd.mm.YYYY"}, {"Name": "Day_Name", "Type": "str", "Examples": ["Monday", "Wednesday", "Friday", "Thursday", "Monday", "Tuesday"], "Enum": ["Monday", "Tuesday", "Wednesday", "Thursday", "Friday", "Saturday", "Sunday"]}]}, {"Name": "Date_Period", "Representations": [{"Name": "Specific_Period", "Type": "str", "Examples": ["01.01.2024 - 31.01.2024", "01.06.2023 - 30.06.2023", "01.12.2022 - 31.12.2022"], "Pattern": "dd.mm.YYYY - dd.mm.YYYY"}, {"Name": "Month", "Type": "str", "Examples": ["January", "June", "December"], "Enum": ["January", "February", "March", "April", "May", "June", "July", "August", "September", "October", "November", "December"]}, {"Name": "Quarter", "Type": "str", "Examples": ["Q1", "Q2", "Q3"], "Enum": ["Q1", "Q2", "Q3", "Q4"]}, {"Name": "Season", "Type": "str", "Examples": ["Winter", "Summer", "Autumn"], "Enum": ["Winter", "Spring", "Summer", "Autumn"]}]}, {"Name": "Destination_Country", "Representations": [{"Name": "Country_Name", "Type": "str", "Examples": ["United States", "Germany", "China"]}, {"Name": "Country_Code", "Type": "str", "Examples": ["US", "DE", "CN"]}, {"Name": "Country_Abbreviation", "Type": "str", "Examples": ["USA", "GER", "CHN"]}]}]
```
As the result, response will be JSON-readable line in the format:
```json
[{"Value": "Corrected search phrase", "Name": "Correct"}, {"Name": "filter-name.representation", "Value": "some-value"}]
```
Field and representation names will be aligned with the provided schema. Example:
```json
[{"Value": "Which logistics companies in the US have a perfect 5.0 rating?", "Name": "Correct"}, {"Name": "Customer_Ratings.Exact_Rating", "Value": 5.0}, {"Name": "Destination_Country.Country_Code", "Value": "US"}]
```
Used for fine-tuning `system` phrases:
```python
[
"Expert at Deconstructing Search Queries",
"Master in Query Analysis",
"Premier Search Query Interpreter",
"Advanced Search Query Decoder",
"Search Query Parsing Genius",
"Search Query Parsing Wizard",
"Unrivaled Query Parsing Mechanism",
"Search Query Parsing Virtuoso",
"Query Parsing Maestro",
"Ace of Search Query Structuring"
]
```
Used for fine-tuning `instruction` phrases:
```python
[
"Convert queries to JSON, align with schema, ensure correct spelling.",
"Analyze and structure queries in JSON, maintain schema, check spelling.",
"Organize queries in JSON, adhere to schema, verify spelling.",
"Decode queries to JSON, follow schema, correct spelling.",
"Parse queries to JSON, match schema, spell correctly.",
"Transform queries to structured JSON, align with schema and spelling.",
"Restructure queries in JSON, comply with schema, accurate spelling.",
"Rearrange queries in JSON, strict schema adherence, maintain spelling.",
"Harmonize queries with JSON schema, ensure spelling accuracy.",
"Efficient JSON conversion of queries, schema compliance, correct spelling."
]
```
### Direct Use
```python
import json
from json import JSONDecodeError
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM
INSTRUCTION_TEMPLATE = """
### System: Master in Query Analysis
### Instruction: Organize queries in JSON, adhere to schema, verify spelling.
#### Category: {0}
#### Schema: ```{1}```
#### Query: {2}
### Response:
"""
def parse(
query: str,
company_category: str,
filter_schema: dict,
model: AutoModelForCausalLM,
tokenizer: AutoTokenizer
):
input_text = INSTRUCTION_TEMPLATE.format(
company_category,
json.dumps(filter_schema),
query
)
input_ids = tokenizer.encode(input_text, return_tensors='pt')
# Generating text
output = model.generate(input_ids.to('cuda'),
max_new_tokens=1024,
do_sample=True,
temperature=0.05,
pad_token_id=50256
)
try:
parsed = json.loads(tokenizer.decode(output[0], skip_special_tokens=True).split('## Response:\n')[-1])
except JSONDecodeError as e:
parsed = dict()
return parsed
```
## Bias, Risks, and Limitations
### Bias
Again, this model was fine-tuned for following the zero-shot query parsing instructions.
So, all ethical biases are inherited by the original model.
Model was fine-tuned to be able to work with the unknown company domain and filters schema. But, can be better with the training company categories:
Educational Institutions, Job Recruitment Agencies, Banking Services, Investment Services, Insurance Services, Financial Planning and Advisory, Credit Services, Payment Processing, Mortgage and Real Estate Services, Taxation Services, Risk Management and Compliance, Digital and Mobile Banking, Retail Stores (Online and Offline), Automotive Dealerships, Restaurants and Food Delivery Services, Entertainment and Media Platforms, Government Services, Travelers and Consumers, Logistics and Supply Chain Management, Customer Support Services, Market Research Firms, Mobile App Development, Game Development, Cloud Computing Services, Data Analytics and Business Intelligence, Cybersecurity Software, User Interface/User Experience Design, Internet of Things (IoT) Development, Project Management Tools, Version Control Systems, Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment, Issue Tracking and Bug Reporting, Collaborative Development Environments, Team Communication and Chat Tools, Task and Time Management, Customer Support and Feedback, Cloud-based Development Environments, Image Stock Platforms, Video Hosting and Portals, Social Networks, Professional Social Networks, Dating Apps
### Risks and Limitations
Known limitations:
1. Can add extra spaces or remove spaces: `1-2` -> `1 - 2`.
2. Can add extra words: `5` -> `5 years`.
3. Can not differentiate between `<>=` and theirs HTML versions `<`, `>`, `&eq;`.
4. Bad with abbreviations.
5. Can add extra `.0` for floats and integers.
6. Can add extra `0` or remove `0` for integers with a char postfix: `10M` -> `1m`.
7. Can hallucinate with integers. For the case like `list of positions exactly 7 openings available` result can be
`{'Name': 'Job_Type.Exact_Match', 'Value': 'Full Time'}`.
8. We fine-tuned this model with max sequence length = 1024, so it may happen that response will not be JSON-readable.
The list will be extended in the future.
### Recommendations
1. We used synthetic data for the first version of this model. So, we suggest you to precisely test this model on your company's domain, even it's in the list.
2. Use meaningful names for filters and theirs representations.
3. Provide examples for each representation.
4. Try to be compact, model was fine-tuned with max sequence length equal 1024.
5. During the generation use greedy strategy with tempertature 0.05.
6. The result will be better if you align a filters schema with a schema type of the training data.
## How to Get Started with the Model
Use the code below to get started with the model.
```python
MODEL_ID = 'EmbeddingStudio/query-parser-falcon-7b-instruct'
```
Initialize tokenizer:
```python
from transformers import AutoTokenizer
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(
MODEL_ID,
trust_remote_code=True,
add_prefix_space=True,
use_fast=False,
)
```
Initialize model:
```python
import torch
from peft import LoraConfig
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, BitsAndBytesConfig
peft_config = LoraConfig(
lora_alpha=16,
lora_dropout=0.1,
r=64,
bias="none",
task_type="CAUSAL_LM",
)
bnb_config = BitsAndBytesConfig(
load_in_4bit=True,
load_4bit_use_double_quant=True,
bnb_4bit_quant_type="nf4",
bnb_4bit_compute_dtype=torch.bfloat16,
)
device_map = {"": 0}
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
MODEL_ID,
quantization_config=bnb_config,
device_map=device_map,
torch_dtype=torch.float16
)
```
Use for parsing:
```python
import json
from json import JSONDecodeError
INSTRUCTION_TEMPLATE = """
### System: Master in Query Analysis
### Instruction: Organize queries in JSON, adhere to schema, verify spelling.
#### Category: {0}
#### Schema: ```{1}```
#### Query: {2}
### Response:
"""
def parse(
query: str,
company_category: str,
filter_schema: dict,
model: AutoModelForCausalLM,
tokenizer: AutoTokenizer
):
input_text = INSTRUCTION_TEMPLATE.format(
company_category,
json.dumps(filter_schema),
query
)
input_ids = tokenizer.encode(input_text, return_tensors='pt')
# Generating text
output = model.generate(input_ids.to('cuda'),
max_new_tokens=1024,
do_sample=True,
temperature=0.05,
pad_token_id=50256
)
try:
parsed = json.loads(tokenizer.decode(output[0], skip_special_tokens=True).split('## Response:\n')[-1])
except JSONDecodeError as e:
parsed = dict()
return parsed
category = 'Logistics and Supply Chain Management'
query = 'Which logistics companies in the US have a perfect 5.0 rating ?'
schema = [{"Name": "Customer_Ratings", "Representations": [{"Name": "Exact_Rating", "Type": "float", "Examples": [4.5, 3.2, 5.0, "4.5", "Unstructured"]}, {"Name": "Minimum_Rating", "Type": "float", "Examples": [4.0, 3.0, 5.0, "4.5"]}, {"Name": "Star_Rating", "Type": "int", "Examples": [4, 3, 5], "Enum": [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]}]}, {"Name": "Date", "Representations": [{"Name": "Day_Month_Year", "Type": "str", "Examples": ["01.01.2024", "15.06.2023", "31.12.2022", "25.12.2021", "20.07.2024", "15.06.2023"], "Pattern": "dd.mm.YYYY"}, {"Name": "Day_Name", "Type": "str", "Examples": ["Monday", "Wednesday", "Friday", "Thursday", "Monday", "Tuesday"], "Enum": ["Monday", "Tuesday", "Wednesday", "Thursday", "Friday", "Saturday", "Sunday"]}]}, {"Name": "Date_Period", "Representations": [{"Name": "Specific_Period", "Type": "str", "Examples": ["01.01.2024 - 31.01.2024", "01.06.2023 - 30.06.2023", "01.12.2022 - 31.12.2022"], "Pattern": "dd.mm.YYYY - dd.mm.YYYY"}, {"Name": "Month", "Type": "str", "Examples": ["January", "June", "December"], "Enum": ["January", "February", "March", "April", "May", "June", "July", "August", "September", "October", "November", "December"]}, {"Name": "Quarter", "Type": "str", "Examples": ["Q1", "Q2", "Q3"], "Enum": ["Q1", "Q2", "Q3", "Q4"]}, {"Name": "Season", "Type": "str", "Examples": ["Winter", "Summer", "Autumn"], "Enum": ["Winter", "Spring", "Summer", "Autumn"]}]}, {"Name": "Destination_Country", "Representations": [{"Name": "Country_Name", "Type": "str", "Examples": ["United States", "Germany", "China"]}, {"Name": "Country_Code", "Type": "str", "Examples": ["US", "DE", "CN"]}, {"Name": "Country_Abbreviation", "Type": "str", "Examples": ["USA", "GER", "CHN"]}]}]
output = parse(query, category, schema)
print(output)
# [out]: [{"Value": "Which logistics companies in the US have a perfect 5.0 rating?", "Name": "Correct"}, {"Name": "Customer_Ratings.Exact_Rating", "Value": 5.0}, {"Name": "Destination_Country.Country_Code", "Value": "US"}]
```
## Training Details
### Training Data
We used synthetically generated query parsing instructions:
* We generated lists of possible filters for 63 customer categories:
* [Raw version of filters dataset](https://huggingface.co/datasets/EmbeddingStudio/synthetic-search-filters-raw)
* [Split by representations](https://huggingface.co/datasets/EmbeddingStudio/synthetic-search-filters)
* Select randomly up-to 150 possible combinations (1-3 filters in each combination) of filters, the way each filter's representation appears maximum twice.
* For a given category and combination we [generated](https://huggingface.co/datasets/EmbeddingStudio/synthetic-search-queries) with GPT-4 Turbo:
* 2 search queries and theirs parsed version with unstructured parts.
* 2 search queries and theirs parsed version without unstructured part.
* Using filters, queries and parsed version we prepared [72.5k falcon format instruction](EmbeddingStudio/query-parsing-instructions-falcon)
**Warning:** EmbeddingStudio team aware you that generated queries **weren't enough curated**, and will be curated later once we finish our product market fit stage.
#### Principles of train / test splitting
As we are trying to fine-tune LLM to follow zero-shot query parsing instructions, so we want to test:
* Ability to work well with unseen domain
* Ability to work well with unseen filters
* Ability to work well with unseen queries
For these purposes we:
1. We put into test split 5 categories, completely separared from train: `Telecommunication Companies, Legal Services, Enterprise Software Development, Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning, Documentation and Knowledge Sharing`.
2. Also out of each appearing in train company categories, we put aside / removed one filter and queries related to it.
3. Selected 5% of other queries and put it into test.
#### Filters generation details
We used GPT-4 Turbo to generate several possible filters for 63 company categroies. For each filter we also generated some possible representations. For examples filter `Date` can be represented as `dd/mm/YYYY`, `YYYY-mm-dd`, as words `2024 Jan 17`, etc.
#### Queries generation details
We also used GPT-4 Turbo for generation of search queries and theirs parsed version. Main principles were:
* If passed schema doesn't contain possible filter, do not generate query itself or a possible filter
* If a selected representations combination contains enumeration, so we ask to map values in a search query and a parsed version.
* If a selected representations combination contains pattern, so we ask GPT-4 Turbo to be aligned with a pattern
#### Instructions generation details
For the generation instructions we used following ideas:
1. Zero-Shot query parser should be schema agnostic. Cases like `snake_case, CamelCase, http-headers-like` should not ruin generation process.
2. Zero-Shot query parser should be spelling errors insensitive.
3. Training instructions should be in the following order:
* Category
* Schema
* Query
So LLM can be used in the following way: just generate embedding of category -> schema part, so inference will be faster.
We assume, that `schema agnostic` termin means something wider, like to be able to work not only with JSONs, but also with HTML, Markdown, YAML, etc. We are working on it.
So, what was our approach as an attempt to achieve these abilities:
1. For each query we generated a version with a mistake
2. Passed to each parsed version an additional field `Correct`, which contains a corrected version of a search query.
3. For each query we randomly selected and used a case for schema fields and a case for filter and representation names.
4. For each query we additionally generated two instuctions:
* Where did we remove from a provided schema and parsed version one filter
* Where did we remove from a provided schema and parsed version all related filters
**Warning:** EmbeddingStudio team ask you to curate datasets on your own precisely.
### Training Procedure
1. Mixed Precision Regime
2. Supervised Fine-Tuning
3. Three epochs with cosine scheduler
All details in Training Hyperparameters
#### Preprocessing [optional]
The preprocessing steps are not detailed in the provided code. Typically, preprocessing involves tokenization, normalization, data augmentation, and handling of special tokens. In this training setup, the tokenizer was configured with `add_prefix_space=True` and `use_fast=False`, which might indicate special considerations for tokenizing certain languages or text formats.
#### Training Hyperparameters
| Hyperparameter | Value | Description |
|--------------------------------------|------------------------------|-------------------------------------------------------|
| **Training Regime** | Mixed Precision (bfloat16) | Utilizes bfloat16 for efficient memory usage and training speed. |
| **Model Configuration** | Causal Language Model | Incorporates LoRA (Low-Rank Adaptation) for training efficiency. |
| **Quantization Configuration** | Bits and Bytes (BnB) | Uses settings like `load_in_4bit` and `bnb_4bit_quant_type` for model quantization. |
| **Training Environment** | CUDA-enabled Device | Indicates GPU acceleration for training. |
| **Learning Rate** | 2e-4 | Determines the step size at each iteration while moving toward a minimum of a loss function. |
| **Weight Decay** | 0.001 | Helps in regularizing and preventing overfitting. |
| **Warmup Ratio** | 0.03 | Fraction of total training steps used for the learning rate warmup. |
| **Optimizer** | Paged AdamW (32-bit) | Optimizes the training process with efficient memory usage. |
| **Gradient Accumulation Steps** | 2 | Reduces memory consumption and allows for larger effective batch sizes. |
| **Max Grad Norm** | 0.3 | Maximum norm for the gradients. |
| **LR Scheduler Type** | Cosine | Specifies the learning rate schedule. |
| **PEFT Configurations** | LoraConfig | Details like `lora_alpha`, `lora_dropout`, and `r` for LoRA adaptations. |
| **Training Dataset Segmentation** | Train and Test Sets | Segmentation of the dataset for training and evaluation. |
| **Max Sequence Length** | 1024 | Maximum length of the input sequences. |
### Testing Data, Factors & Metrics
#### Testing Data
All information is provided in [Training Data](#training-data) section.
### Factors Influencing Falcon-7B-Instruct Model Performance
#### 1. Company Category and Domain Knowledge
- Performance may vary based on the specific company category or domain.
- Enhanced performance in domains specifically trained on, such as Educational Institutions, Banking Services, Logistics, etc.
#### 2. Filter Schema Adaptability
- Ability to adapt to various filter schemas.
- Performance in parsing and organizing queries according to different schemas.
#### 3. Handling of Spelling and Syntax Errors
- Robustness in handling spelling errors and syntax variations in queries.
#### 4. Representation and Type Handling
- Capability to handle different data representations (e.g., date formats, enumerations, patterns).
- Accurate processing of various base types (int, float, str, bool).
#### 5. Length and Complexity of Queries
- Impact of the length and complexity of queries on performance.
- Maximum sequence length of 1024 could pose limitations for longer or complex queries.
#### 6. Bias and Ethical Considerations
- Inherited ethical biases from the original model.
- Importance of understanding these biases in different contexts.
#### 7. Limitations in Fine-Tuning and Data Curation
- Limitations such as extra spaces, handling of abbreviations, etc.
- Influence of the extent of training data curation on model accuracy.
#### 8. Specific Use Cases
- Recommended primarily for zero-shot search query parsing and search query spell correction.
- Performance in other use cases might be unpredictable.
#### 9. Training Data Quality and Diversity
- Quality and diversity of synthetic training data.
- Influence on the model's effectiveness across different scenarios.
##### Testing Procedure
Results of testing procedure as JSON is provided [here](https://huggingface.co/EmbeddingStudio/query-parser-falcon-7b-instruct/blob/main/falcon-7b-instruct-test.json).
This is a list of items, each item is:
1. Predicted parsed query
2. Real parsed query
3. Category
#### Metrics
#### Metric Overview
Our zero-shot search query parsing model is designed to extract structured information from unstructured search queries with high precision. The primary metric for evaluating our model's performance is the True Positive (TP) rate, which is assessed using a specialized token-wise Levenshtein distance. This approach is aligned with our goal to achieve semantic accuracy in parsing user queries.
#### True Positives (TP)
- **Definition**: A True Positive in our model is counted when the model correctly identifies both the 'Name' and 'Value' in a query, matching the expected results.
- **Measurement Method**: The TP rate is quantified using the `levenshtein_tokenwise` function, which calculates the distance between predicted and actual key-value pairs at a token level. We consider a Levenshtein distance of 0.25 or less as acceptable for matching.
- **Importance**:
- **Token-Level Accuracy**: We use token-wise accuracy over traditional character-level Levenshtein distance, which can be overly strict, especially for minor spelling variations. Our token-wise approach prioritizes semantic accuracy.
- **Relevance to Search Queries**: Accuracy at the token level is more indicative of the model's ability to understand and parse user intent in search queries.
#### Generation Strategy
- **Approach**: The model generates responses based on input queries with a maximum token length set to 1000, employing a sampling strategy (do_sample=True), and a low temperature setting of 0.05. This controlled randomness in generation ensures a variety of accurate and relevant responses.
- **Impact on TP**:
- The low temperature setting directly influences the TP rate by reducing the randomness in the model's predictions. With a lower temperature, the model is more likely to choose the most probable word in a given context, leading to more accurate and consistent outputs. This is particularly crucial in search query parsing, where understanding and interpreting user input with high precision is vital.
#### Additional Metrics
- **False Positives (FP) and False Negatives (FN)**: These metrics are monitored to provide a comprehensive view of the model's predictive capabilities.
- **Precision, Recall, F1 Score, Accuracy**: These standard metrics complement our TP-focused assessment, providing a rounded picture of the model's performance in various aspects.
#### Motivation for Metric Choice
- **Alignment with User Intent**: Focusing on token-wise accuracy ensures the model's performance closely mirrors the structure and intent typical in search queries.
- **Robustness Against Query Variations**: This metric approach makes the model adaptable to the varied formulations of real-world search queries.
- **Balancing Precision and Recall**: Our method aims to balance the model's ability not to miss relevant key-value pairs (high recall) while not over-identifying irrelevant ones (high precision).
##### Total metrics
| Category | Recall | Precision | F1 | Accuracy |
| ------------------------------------------------ | ------ | --------- | ----- | -------- |
| Telecommunication Companies [+] | 0.70 | 0.67 | 0.68 | 0.52 |
| Legal Services [+] | 0.80 | 0.74 | 0.77 | 0.63 |
| Enterprise Software Development [+] | 0.78 | 0.71 | 0.74 | 0.59 |
| Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning [+] | 0.77 | 0.78 | 0.78 | 0.63 |
| Documentation and Knowledge Sharing [+] | 0.68 | 0.65 | 0.66 | 0.50 |
| Educational Institutions | 0.55 | 0.51 | 0.53 | 0.36 |
| Job Recruitment Agencies | 0.58 | 0.51 | 0.54 | 0.37 |
| Banking Services | 0.73 | 0.81 | 0.76 | 0.62 |
| Investment Services | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.33 |
| Insurance Services | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.62 |
| Financial Planning and Advisory | 0.65 | 0.67 | 0.66 | 0.49 |
| Credit Services | 0.60 | 0.65 | 0.63 | 0.45 |
| Payment Processing | 0.79 | 0.74 | 0.76 | 0.62 |
| Mortgage and Real Estate Services | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Taxation Services | 0.52 | 0.57 | 0.54 | 0.37 |
| Risk Management and Compliance | 1.00 | 0.95 | 0.98 | 0.95 |
| Digital and Mobile Banking | 0.72 | 0.71 | 0.71 | 0.55 |
| Retail Stores (Online and Offline) | 0.96 | 0.87 | 0.92 | 0.85 |
| Automotive Dealerships | 0.52 | 0.53 | 0.53 | 0.36 |
| Restaurants and Food Delivery Services | 0.76 | 0.77 | 0.76 | 0.62 |
| Entertainment and Media Platforms | 0.80 | 0.84 | 0.82 | 0.70 |
| Government Services | 0.58 | 0.65 | 0.61 | 0.44 |
| Travelers and Consumers | 0.89 | 0.89 | 0.89 | 0.80 |
| Logistics and Supply Chain Management | 0.56 | 0.59 | 0.58 | 0.41 |
| Customer Support Services | 0.60 | 0.54 | 0.57 | 0.40 |
| Market Research Firms | 0.52 | 0.49 | 0.51 | 0.34 |
| Mobile App Development | 0.81 | 0.79 | 0.80 | 0.67 |
| Game Development | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.88 |
| Cloud Computing Services | 0.64 | 0.62 | 0.63 | 0.46 |
| Data Analytics and Business Intelligence | 0.63 | 0.61 | 0.62 | 0.45 |
| Cybersecurity Software | 0.54 | 0.59 | 0.57 | 0.39 |
| User Interface/User Experience Design | 0.63 | 0.64 | 0.63 | 0.46 |
| Internet of Things (IoT) Development | 0.89 | 0.71 | 0.79 | 0.65 |
| Project Management Tools | 0.80 | 0.83 | 0.81 | 0.69 |
| Version Control Systems | 0.77 | 0.73 | 0.75 | 0.60 |
| Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment | 0.85 | 0.83 | 0.84 | 0.72 |
| Issue Tracking and Bug Reporting | 0.64 | 0.62 | 0.63 | 0.46 |
| Collaborative Development Environments | 0.68 | 0.67 | 0.68 | 0.51 |
| Team Communication and Chat Tools | 0.94 | 0.91 | 0.93 | 0.87 |
| Task and Time Management | 0.78 | 0.78 | 0.78 | 0.64 |
| Customer Support and Feedback | 0.88 | 0.82 | 0.85 | 0.74 |
| Cloud-based Development Environments | 0.81 | 0.81 | 0.81 | 0.68 |
| Image Stock Platforms | 0.88 | 0.85 | 0.87 | 0.76 |
| Video Hosting and Portals | 0.86 | 0.88 | 0.87 | 0.77 |
| Social Networks | 0.60 | 0.57 | 0.59 | 0.41 |
| Professional Social Networks | 0.68 | 0.69 | 0.68 | 0.52 |
| Dating Apps | 0.90 | 0.90 | 0.90 | 0.82 |
| Aggregate | 0.73 | 0.72 | 0.73 | 0.59 |
##### Unseen domains metrics
| Category | Recall | Precision | F1 | Accuracy |
| ------------------------------------------------ | ------ | --------- | ----- | -------- |
| Telecommunication Companies [+] | 0.70 | 0.67 | 0.68 | 0.52 |
| Legal Services [+] | 0.80 | 0.74 | 0.77 | 0.63 |
| Enterprise Software Development [+] | 0.78 | 0.71 | 0.74 | 0.59 |
| Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning [+] | 0.77 | 0.78 | 0.78 | 0.63 |
| Documentation and Knowledge Sharing [+] | 0.68 | 0.65 | 0.66 | 0.50 |
| Aggregate | 0.75 | 0.71 | 0.73 | 0.57 |
### Results
[More Information Needed]
#### Summary
[More Information Needed]
## Environmental Impact
<!-- Total emissions (in grams of CO2eq) and additional considerations, such as electricity usage, go here. Edit the suggested text below accordingly -->
Carbon emissions can be estimated using the [Machine Learning Impact calculator](https://mlco2.github.io/impact#compute) presented in [Lacoste et al. (2019)](https://arxiv.org/abs/1910.09700).
- **Hardware Type:** NVIDIA Tesla V100
- **Hours used:** 72
- **Cloud Provider:** Google Cloud
- **Compute Region:** us-west-1
- **Carbon Emitted:** 6.48
## Technical Specifications [optional]
### Model Architecture and Objective
[More Information Needed]
### Compute Infrastructure
[More Information Needed]
#### Hardware
[More Information Needed]
#### Software
* Python 3.9+
* CUDA 11.7.1
* NVIDIA [Compatible Drivers](https://www.nvidia.com/download/find.aspx)
* Torch 2.0.0
## More Information / About us
EmbeddingStudio is an innovative open-source framework designed to seamlessly convert a combined
"Embedding Model + Vector DB" into a comprehensive search engine. With built-in functionalities for
clickstream collection, continuous improvement of search experiences, and automatic adaptation of
the embedding model, it offers an out-of-the-box solution for a full-cycle search engine.
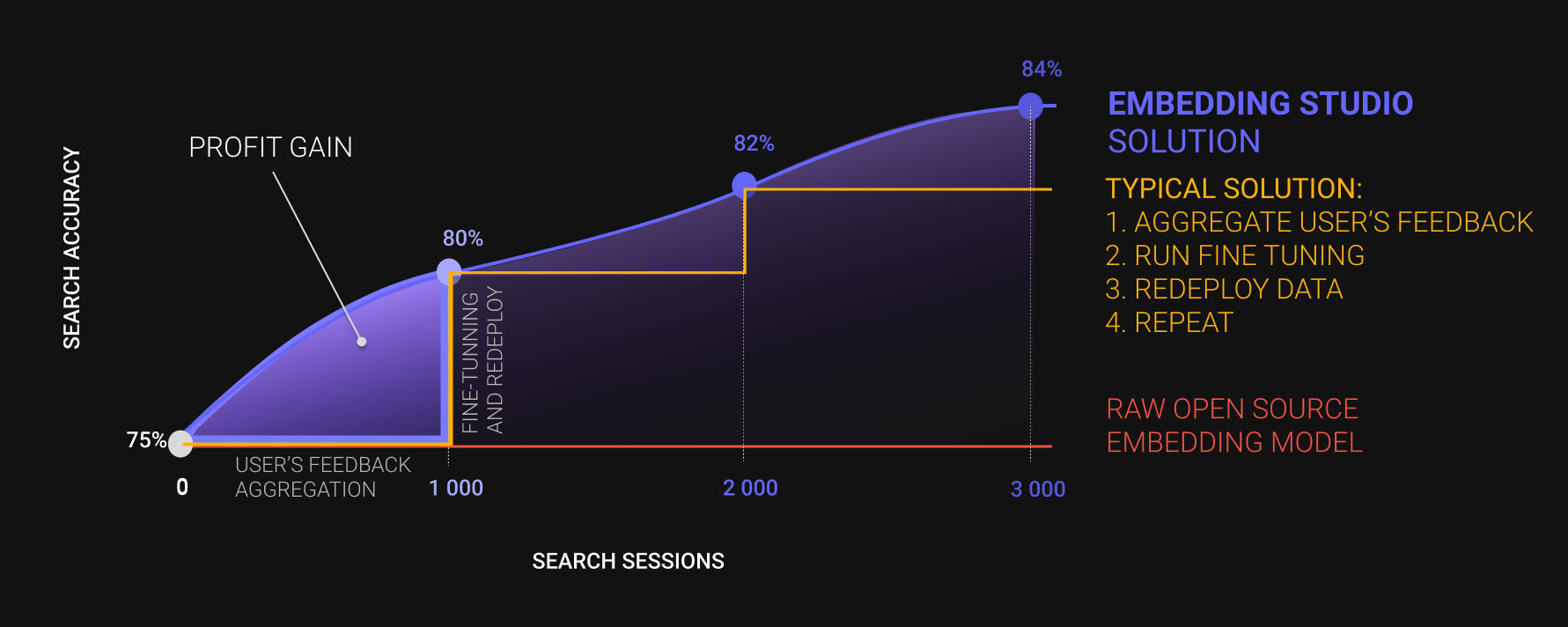
### Features
1. 🔄 Turn your vector database into a full-cycle search engine
2. 🖱️ Collect users feedback like clickstream
3. 🚀 (*) Improve search experience on-the-fly without frustrating wait times
4. 📊 (*) Monitor your search quality
5. 🎯 Improve your embedding model through an iterative metric fine-tuning procedure
6. 🆕 (*) Use the new version of the embedding model for inference
(*) - features in development
EmbeddingStudio is highly customizable, so you can bring your own:
1. Data source
2. Vector database
3. Clickstream database
4. Embedding model
For more details visit [GitHub Repo](https://github.com/EulerSearch/embedding_studio/tree/main).
## Model Card Authors and Contact
* Aleksandr Iudaev [[LinkedIn](https://www.linkedin.com/in/alexanderyudaev/)] [[Email](mailto:[email protected])]
* Andrei Kostin [[LinkedIn](https://www.linkedin.com/in/andrey-kostin/)] [[Email](mailto:[email protected])]
* ML Doom [AI Assistant]
### Framework versions
- PEFT 0.5.0
- Datasets 2.16.1
- BitsAndBytes 0.41.0
- PyTorch 2.0.0
- Transformers 4.36.2
- TRL 0.7.7 |